Are you a motorcycle enthusiast seeking the perfect ride? Curious about the differences between the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines?
Look no further! In this blog post, we’ll dive into the heart of the matter and explore the unique characteristics and performance of these two legendary Harley-Davidson engines.
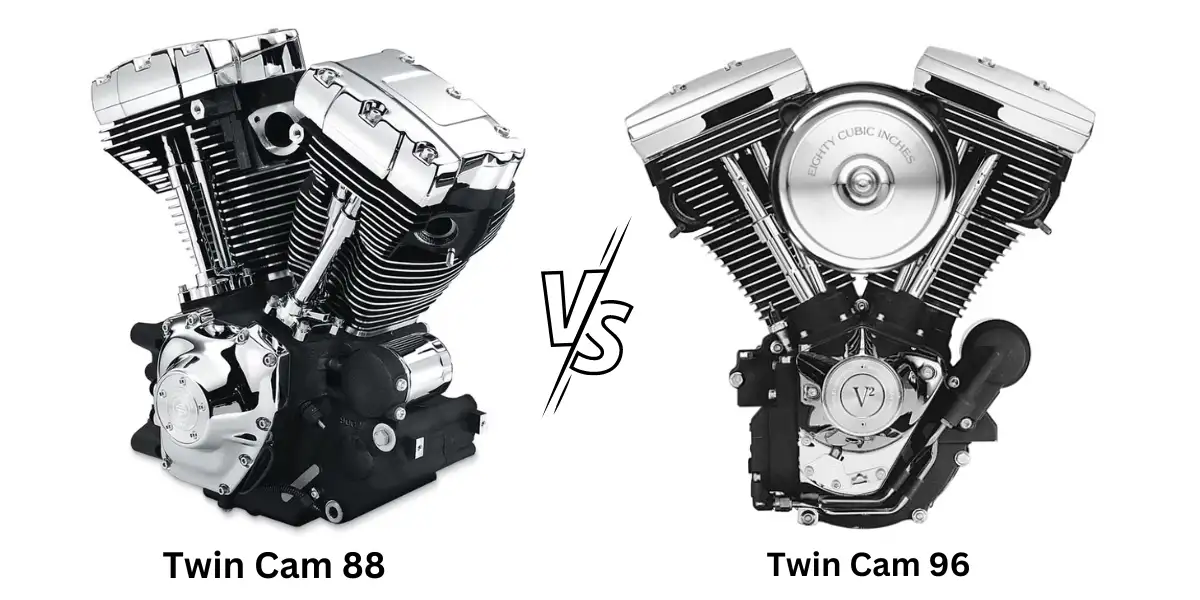
A Quick Comparison Between Twin Cam 88 Vs 96
| Features | Twin Cam 88 | Twin Cam 96 |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement | 1450cc (88.4 cu in) | 1584cc (96.7 cu in) |
| Valve Control | Controlled by a camshaft | Controlled by a camshaft |
| Valve Opening/Closing | Controlled by the camshaft | Controlled by the camshaft |
| Bearing/Tensioner | Known for bearing or tensioner problems | Improved bearing/tensioner system |
| Stock Power | Good power output | Slightly less stock power |
| Manufacturing | Interchangeable cylinders and castings | Interchangeable cylinders and castings |
| Year of Introduction | Introduced in the 1990s | A later version of Twin Cam 88 |
| Popular Applications | Harley-Davidson motorcycles | Harley-Davidson motorcycles |
| Performance Upgrades | Various aftermarket performance upgrades are available | Various aftermarket performance upgrades are available |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate fuel efficiency | Moderate fuel efficiency |
Detailed Comparison Between Twin Cam 88 Vs 96

Displacement:
The displacement of an engine refers to the total volume of all the cylinders in the engine. In the case of the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines, there is a notable difference in displacement.
The Twin Cam 88 engine has a displacement of 1450cc (88.4 cu in), which means the combined volume of all its cylinders is 1450 cubic centimeters or 88.4 cubic inches.
On the other hand, the Twin Cam 96 engine boasts a larger displacement of 1584cc (96.7 cu in), indicating a greater combined volume of its cylinders at 1584 cubic centimeters or 96.7 cubic inches.
Number of Cylinders:
The number of cylinders in an engine directly influences its performance characteristics.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines feature a V-twin configuration, which means they have two cylinders arranged in a V shape.
Consequently, both engines offer the same number of cylinders, providing a balanced power delivery and smooth operation.
Valve Configuration:

The valve configuration determines the number and arrangement of intake and exhaust valves in the engine.
In the case of the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines, they employ a twin camshaft setup, with each cylinder featuring two valves.
This configuration is often referred to as the “overhead valve” (OHV) or “pushrod” design.
The twin camshafts actuate the valves, allowing efficient airflow in and out of the combustion chamber, promoting optimal engine performance.
Valve Control Mechanism:
The valve control mechanism manages the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves, crucial for proper engine operation.
In the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines, the valve control is achieved through the camshafts.
These camshafts are responsible for actuating the valves, allowing precise timing and control over the combustion process. The camshafts ensure that the valves open and close at the right moments, optimizing engine performance.
Ignition System:
The ignition system ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, providing the necessary spark for combustion.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines typically employ electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems with electronic ignition. These modern ignition systems ensure reliable and efficient combustion.
The EFI system delivers the right amount of fuel to the combustion chamber, while the electronic ignition system provides a spark at the right time, promoting smooth and consistent engine operation.
Cooling System:
Efficient cooling is essential for maintaining engine performance and longevity. The Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines rely on an air-cooled design, which means they utilize fins and airflow to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Air-cooled engines are known for their simplicity and reliability. The fins on the engine’s exterior surface increase the surface area, allowing heat to dissipate into the surrounding air.
Adequate airflow, either through natural means or aided by fans, helps in cooling the engine, ensuring it operates within the optimal temperature range.
Fuel Delivery System

The fuel delivery system is a crucial aspect to consider when comparing the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines.
Both engines utilize a sequential port fuel injection (SPFI) system, ensuring precise fuel delivery for optimal performance.
The SPFI system incorporates injectors located near the intake valves, allowing for efficient fuel atomization and distribution. This precise fuel delivery promotes smooth combustion and power output, contributing to the engines’ overall performance.
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is a fundamental factor that affects engine efficiency and power output. The Twin Cam 88 engine features a compression ratio of 8.9:1, while the Twin Cam 96 engine boasts a higher compression ratio of 9.2:1.
A higher compression ratio in the Twin Cam 96 engine allows for better combustion efficiency and potential power gains. It results in improved throttle response and overall engine performance.
The higher compression ratio means that the air-fuel mixture is compressed to a smaller volume before combustion, maximizing the power extracted from each combustion cycle.
Bore and Stroke Dimensions
The bore and stroke dimensions of an engine play a vital role in determining its overall displacement and power characteristics.
The Twin Cam 88 engine features a bore size of 3.75 inches and a stroke length of 4 inches, resulting in a displacement of 1450cc (88.4 cu in).
On the other hand, the Twin Cam 96 engine boasts a larger bore size of 3.75 inches and an increased stroke length of 4.38 inches, leading to a displacement of 1584cc (96.7 cu in).
This larger displacement in the Twin Cam 96 engine allows for potential power gains and improved low-end torque. The increased bore size and stroke length enable a larger air-fuel mixture volume, enhancing the engine’s power output.
Power Output
Power output is a crucial consideration when evaluating motorcycle engines. The Twin Cam 88 engine is renowned for its respectable power delivery, producing a solid amount of horsepower suitable for various riding conditions.
However, the Twin Cam 96 engine offers a slight improvement in power output, potentially delivering a bit more horsepower compared to its predecessor.
This extra power can enhance acceleration and overall performance. The increased displacement and other design improvements contribute to the enhanced power output of the Twin Cam 96 engine.
Torque Output
Torque is the rotational force that determines an engine’s ability to deliver low-end power and acceleration. The Twin Cam 88 engine is known for its robust torque output, providing ample low-end grunt for responsive riding.
However, on average, this engine produces a maximum torque output of approximately 80-85 lb-ft.
On the other hand, the Twin Cam 96 engine, with its larger displacement and potential power gains, may offer improved torque delivery, delivering even better low-end performance.
The Twin Cam 96 engine produces 94 lb-ft of torque at 3,500 rpm. This torque curve remains relatively flat up to around 5,500 rpm before gradually decreasing.
The increased displacement and other design enhancements allow the Twin Cam 96 engine to generate more torque, improving its low-end power and acceleration capabilities.
Manufacturing Period
The manufacturing period refers to the time frame in which the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines were produced. The Twin Cam 88 was introduced in the 1990s, while the Twin Cam 96 is a later version that was produced in 2017.
The Twin Cam 88 engine has a longer manufacturing history and has been utilized in various Harley-Davidson models for several years.
On the other hand, the Twin Cam 96 engine is a more recent iteration, incorporating advancements in technology and design.
Popularity Among Harley-Davidson Riders
The popularity of an engine model among Harley-Davidson riders can indicate its acceptance and satisfaction within the motorcycle community.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 have gained popularity among enthusiasts and riders.
Harley-Davidson riders appreciate the performance, reliability, and distinctive sound characteristics of both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines.
The engines have been widely used in various Harley-Davidson motorcycle models and have garnered a loyal following among riders.
Availability of Aftermarket Upgrades
Aftermarket upgrades play a crucial role in customizing and enhancing the performance of Harley-Davidson motorcycles.
The availability of aftermarket upgrades can determine the range of modifications and improvements that can be made to an engine.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines have a wide range of aftermarket upgrades available. These upgrades include performance enhancements, exhaust systems, air intake kits, engine tuners, and more.
The availability of aftermarket upgrades provides riders with the flexibility to personalize their motorcycles and further improve their performance.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is an important consideration for riders, as it affects the overall cost of ownership and environmental impact.
The fuel efficiency of an engine is influenced by various factors such as design, displacement, and tuning.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines offer comparable fuel efficiency within the context of their respective displacements and power outputs.
While the Twin Cam 96 engine may provide slightly better fuel efficiency due to advancements in technology and design, the difference is not significant.
To maximize fuel efficiency, riders can adopt efficient riding techniques such as smooth acceleration, maintaining steady speeds, and regular maintenance of the motorcycle.
Emissions Compliance
In today’s environmentally conscious world, meeting emissions regulations is crucial for motorcycle manufacturers. Emissions compliance ensures that the engine meets the required standards for air pollution control.
Both the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 engines are designed to meet emissions regulations, featuring modern fuel injection systems and catalytic converters.
These components help in reducing harmful emissions, ensuring that the engines comply with the necessary environmental standards.
Harley-Davidson prioritizes environmental responsibility and works towards developing engines that are both powerful and environmentally friendly.
Performance Comparison: Twin Cam 88 Vs. Twin Cam 96
The overall performance of a motorcycle engine depends on several factors, including power delivery, torque, and how well it complements the motorcycle’s chassis and suspension.
In terms of overall performance, the Twin Cam 96 engine offers a noticeable improvement over the Twin Cam 88.
The increased power and torque of the Twin Cam 96 provide a more thrilling riding experience, allowing you to effortlessly tackle challenging terrains and enjoy spirited rides on highways or twisty roads.
The Twin Cam 96 engine’s enhanced performance makes it an attractive choice for riders seeking a powerful and dynamic motorcycle.
FAQs
Q. Can I Feel A Noticeable Difference In Riding Experience Between Twin Cam 88 And Twin Cam 96?
A: Yes, riders often notice a difference in the riding experience between Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 motorcycles.
The Twin Cam 96’s increased power and torque can provide a more responsive and energetic ride compared to the Twin Cam 88.
Q. What Is The Difference Between Twin Cam 88 And Twin Cam 96?
A: The main difference between Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96 is the engine displacement.
The Twin Cam 88 has an 88 cubic inch (1,450 cc) engine, while the Twin Cam 96 has a larger 96 cubic inch (1,584 cc) engine.
Q. Which One Is More Powerful, Twin Cam 88 Or Twin Cam 96?
A: The Twin Cam 96 is generally more powerful than the Twin Cam 88 due to its larger engine displacement.
The larger displacement allows for more air and fuel to be burned, resulting in increased power output.
Q. Are There Any Performance Differences Between Twin Cam 88 And Twin Cam 96?
A: Yes, there are performance differences between the Twin Cam 88 and Twin Cam 96.
The Twin Cam 96 generally offers improved acceleration and overall performance compared to the Twin Cam 88, thanks to its larger engine size.
Q. Can I Upgrade From A Twin Cam 88 To A Twin Cam 96?
A: Yes, it is possible to upgrade a Twin Cam 88 to a Twin Cam 96.
However, it is important to note that this may involve significant modifications and expenses, including replacing the engine and making corresponding adjustments to the bike’s components.
Conclusion
When it comes to the Twin Cam 88 versus the Twin Cam 96, choosing the right engine for your motorcycle can make a noticeable difference in your riding experience.
With its larger engine displacement, the Twin Cam 96 offers more power and improved performance, giving you an exhilarating and responsive ride.
Whether you’re seeking enhanced acceleration or simply want to make a bold statement on the road, the Twin Cam 96 is the way to go.
Upgrade your riding experience and unleash the full potential of your motorcycle with the impressive Twin Cam 96 engine.
