Are you struggling to start your car? It could be due to a bad starter or fuel pump. These are common issues that can leave you stranded and frustrated.
But how do you know which one is the culprit? In short, a bad starter will make a clicking sound or no sound at all, while a faulty fuel pump will cause the engine to crank but not start.
In this article, we will dive deeper into the differences between a bad starter and a fuel pump, and how to diagnose and fix them. Let’s get started and get you back on the road!
Signs of a Bad Starter
Identifying signs of a bad starter is essential to prevent car problems from escalating.

A starter motor is an electric motor that initiates the engine’s rotation when you turn the ignition key.
If the starter is faulty, you may experience difficulty starting your car, a clicking noise, or no response from the engine at all.
Here are some signs to watch out for that indicates your starter may be bad.
Grinding Noise
The noise is usually caused by worn-out gears or the starter motor’s inability to engage with the flywheel.
This can cause damage to both the starter and the flywheel if not addressed promptly.
If you hear a grinding noise when starting your car, it’s best to have a professional mechanic inspect it.
Flickering Dashboard Lights
When the starter motor draws too much power from the battery, it can cause the dashboard lights to flicker or dim.
This is because the battery is unable to provide enough power to start the engine.
If you notice your dashboard lights flickering or dimming when you turn the ignition key, it’s time to have your starter checked.
Slow Cranking
If you hear a slow cranking noise when starting your car, it’s a sign that the starter is not working correctly.
The engine may still start, but it will take longer than usual. A slow cranking noise can be caused by a weak battery, but it can also be due to a bad starter.
If you experience slow cranking, it’s best to have your car inspected by a professional mechanic.
Clicking Noise
A clicking noise when you turn the ignition key is another sign of a bad starter.
This noise is caused by the starter solenoid not receiving enough power from the battery. The solenoid is responsible for engaging the starter motor with the flywheel.
If it’s not getting enough power, it won’t engage, and you’ll hear a clicking noise instead.
If you hear a clicking noise when you turn the ignition key, have your starter inspected by a professional mechanic.
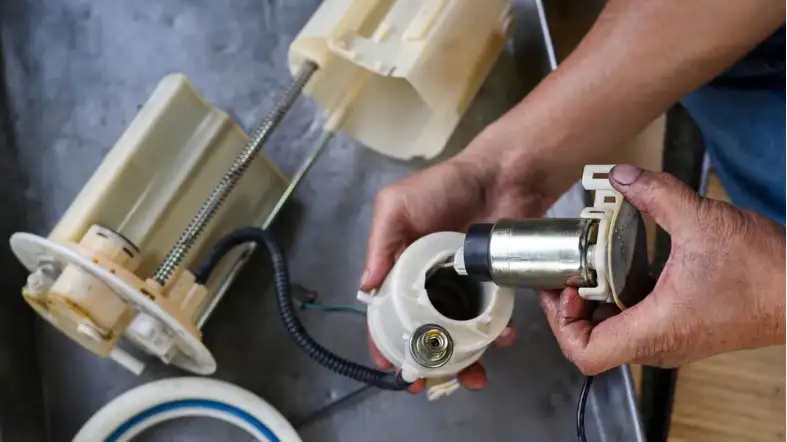
Symptoms of a Failing Fuel Pump

Identifying the symptoms of a failing fuel pump is crucial for maintaining the health of your vehicle’s engine.
The fuel pump is responsible for pumping fuel from the gas tank to the engine.
If it fails, the engine may not receive enough fuel, causing it to run poorly or even stall. Here are some common symptoms of a failing fuel pump to watch out for:
Difficulty Starting the Engine
If your vehicle is having difficulty starting, it could be a sign of a failing fuel pump.
The fuel pump supplies fuel to the engine, and if it’s not working correctly, the engine may not receive enough fuel to start.
If you notice that your engine is slow to start or won’t start at all, it’s best to have your fuel pump checked.
Engine Sputtering or Stalling
If the fuel pump is not delivering enough fuel to the engine, it can cause the engine to sputter or stall.
This can happen while the engine is idling or when you’re driving at high speeds. If your engine sputters or stalls, it’s time to have your fuel pump inspected.
Loss of Power
When Accelerating If you notice a loss of power when you accelerate, it could be due to a failing fuel pump.
The fuel pump is responsible for supplying fuel to the engine when you press the accelerator pedal.
If it’s not working correctly, the engine may not receive enough fuel, causing a loss of power.
If you experience a loss of power when accelerating, it’s best to have your fuel pump inspected.
Unusual Engine Noise
If you hear a whining noise coming from the fuel tank or engine compartment, it could be a sign of a failing fuel pump.
This noise is caused by the fuel pump working harder than normal to supply fuel to the engine.
If you hear any unusual engine noises, it’s time to have your fuel pump checked.
Common Causes of Starter and Fuel Pump Issues
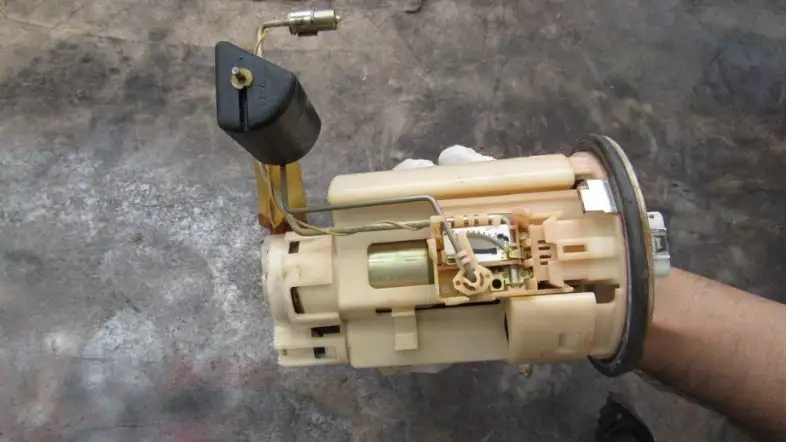
Starter and fuel pump issues are common problems that can occur in vehicles.
Identifying the causes of these issues is crucial for maintaining the health of your vehicle. Here are some common causes of starter and fuel pump issues:
Starter Issues
- Battery Issues: The battery is responsible for supplying power to the starter motor. If the battery is weak or has a low charge, it can cause starter issues. If you experience difficulty starting your vehicle or hear a clicking noise when you turn the ignition key, it could be due to a weak battery.
- Ignition Switch Issues: The ignition switch is responsible for sending power to the starter motor when you turn the ignition key. If the ignition switch is faulty, it can cause starter issues. If you turn the key and nothing happens, it’s time to have your ignition switch checked.
- Starter Motor Issues: The starter motor is responsible for initiating the engine’s rotation when you turn the ignition key. If the starter motor is faulty, it can cause starter issues. If you hear a grinding noise when starting your vehicle or the engine cranks slowly, it’s time to have your starter motor inspected.
Fuel Pump Issues
- Fuel Filter Issues: The fuel filter is responsible for filtering impurities from the fuel before it reaches the fuel pump. If the fuel filter is clogged or dirty, it can cause fuel pump issues. If you experience a loss of power when accelerating or notice a decrease in fuel efficiency, it’s time to have your fuel filter checked.
- Electrical Issues: The fuel pump relies on electrical power to operate. If there’s an issue with the electrical system, it can cause fuel pump issues. If you experience difficulty starting your vehicle or notice a loss of power when accelerating, it could be due to an electrical issue.
- Fuel Contamination: Fuel contamination can occur when debris or impurities enter the fuel system. If this happens, it can cause fuel pump issues. If you notice that your engine is sputtering or stalling, it’s time to have your fuel system inspected for contamination.
How to Test Your Starter
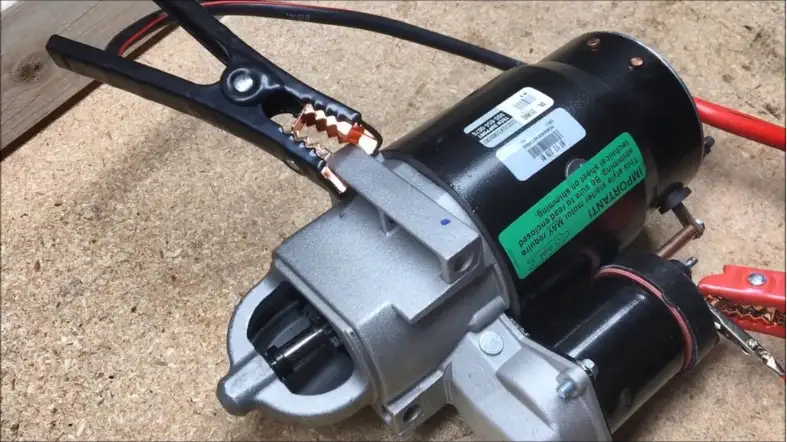

Testing your starter is an important part of vehicle maintenance.
If you suspect that your starter is failing, there are a few simple tests you can perform to confirm the issue. Here are the steps to test your starter:
Check the Battery
Before testing the starter, it’s essential to check the battery. A weak or dead battery can cause starter issues.
Use a voltmeter to check the battery’s voltage. The voltage should be around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is low, it’s time to charge or replace the battery.
Check the Connections
Ensure that the battery connections are clean and secure. Loose or dirty connections can cause starter issues.
Use a wrench to tighten the connections or clean them with a wire brush.
Test the Starter
To test the starter, locate the starter motor under the vehicle. Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the starter’s solenoid.
Connect the multimeter’s red lead to the solenoid’s positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal.
Have someone turn the ignition key while you check the voltage. The voltage should be around 12 volts.
If the voltage is low or nonexistent, it’s time to have your starter inspected by a professional mechanic.
Check the Starter Motor
If the voltage at the solenoid is correct, you can check the starter motor.
Use a jumper cable to connect the starter’s positive terminal to the battery’s positive terminal. Connect the negative terminal to the starter’s housing.
Have someone turn the ignition key while you observe the starter. The starter should spin quickly and smoothly.
If it doesn’t spin or spin slowly, it’s time to have your starter motor inspected by a professional mechanic.
How to Test Your Fuel Pump
Testing your fuel pump is an essential part of vehicle maintenance.
If you suspect that your fuel pump is failing, there are a few simple tests you can perform to confirm the issue. Here are the steps to test your fuel pump:
Check the Fuses and Relays
Before testing the fuel pump, it’s essential to check the fuses and relays. A blown fuse or faulty relay can cause fuel pump issues.
Check the vehicle’s owner’s manual to locate the fuse box and fuel pump relay. Use a multimeter to check the fuses and relays for continuity. Replace any blown fuses or faulty relays.
Check the Fuel Pressure
To check the fuel pressure, locate the fuel pressure test port on the fuel rail. Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the port.
Turn the ignition key to the on position without starting the engine.
The fuel pressure should read around 30-45 PSI. If the pressure is low or nonexistent, it’s time to have your fuel pump inspected by a professional mechanic.
Check the Fuel Pump Voltage
To check the fuel pump voltage, locate the fuel pump connector.
Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the connector. Connect the multimeter’s red lead to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal.
Have someone turn the ignition key while you check the voltage. The voltage should be around 12 volts.
If the voltage is low or nonexistent, it’s time to have your fuel pump inspected by a professional mechanic.
Check the Fuel Pump Relay
If the fuel pump voltage is correct, you can check the fuel pump relay. Locate the fuel pump relay and remove it.
Use a jumper wire to connect the relay’s battery and fuel pump terminals.
Turn the ignition key to the on position without starting the engine. If you hear the fuel pump running, it means the relay is faulty and needs to be replaced.
How to Replace Your Starter
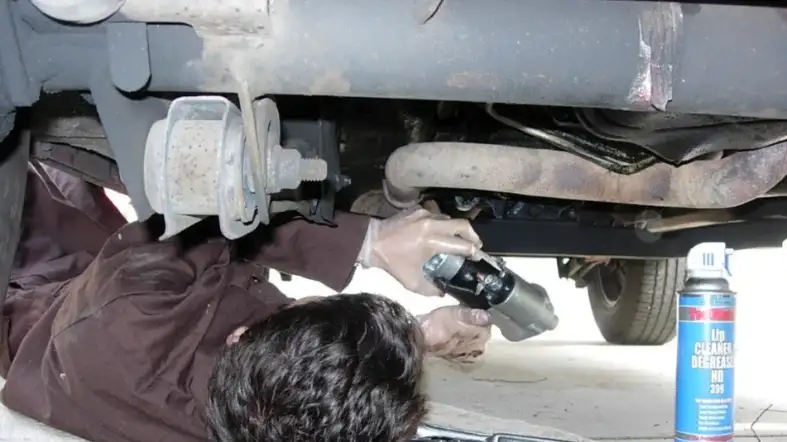

Replacing your starter is a necessary part of vehicle maintenance if your current starter is failing or has failed.
While it may seem daunting, replacing your starter is a relatively straightforward process. Here are the steps to replace your starter:
Gather the Necessary Tools
Before starting the replacement process, gather the necessary tools, including a wrench set, socket set, and a new starter motor.
Disconnect the Battery
To begin the replacement process, disconnect the battery’s negative cable to prevent any electrical shocks or accidents.
Locate the Starter
Locate the starter motor, which is typically located on the engine’s underside.
Remove the Old Starter
Use a wrench or socket set to remove the bolts that hold the starter in place. Disconnect any electrical connections to the starter.
Install the New Starter
Place the new starter motor in the same position as the old starter motor. Use the bolts that came with the new starter to secure it in place.
Reconnect any electrical connections that were disconnected.
Reconnect the Battery
Reconnect the battery’s negative cable.
Test the New Starter
Turn the ignition key to test the new starter motor. The engine should start smoothly without any issues.
How to Replace Your Fuel Pump
Replacing your fuel pump is a necessary part of vehicle maintenance if your current fuel pump is failing or has failed.
While it may seem daunting, replacing your fuel pump is a relatively straightforward process. Here are the steps to replace your fuel pump:
Gather the Necessary Tools
Before starting the replacement process, gather the necessary tools, including a wrench set, socket set, fuel line disconnect tool, and a new fuel pump.
Relieve Fuel Pressure
Before starting the replacement process, relieve the fuel pressure by disconnecting the fuel pump fuse or relay and cranking the engine until it stalls.
Disconnect the Battery
To begin the replacement process, disconnect the battery’s negative cable to prevent any electrical shocks or accidents.
Locate the Fuel Pump
Locate the fuel pump, which is typically located inside the fuel tank.
Remove the Old Fuel Pump
Use a wrench or socket set to remove the bolts or screws that hold the fuel pump in place.
Disconnect any electrical connections and fuel lines from the fuel pump. Use the fuel line disconnect tool to remove any fuel lines.
Install the New Fuel Pump
Place the new fuel pump in the same position as the old fuel pump. Use the bolts or screws that came with the new fuel pump to secure it in place.
Reconnect any electrical connections and fuel lines that were disconnected. Use the fuel line disconnect tool to connect any fuel lines.
Reconnect the Battery
Reconnect the battery’s negative cable.
Test the New Fuel Pump
Turn the ignition key to the on position without starting the engine. Listen for the fuel pump to engage.
Once the pump stops, turn off the ignition. Start the engine and ensure that it runs smoothly without any issues.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Preventative maintenance is essential for keeping your vehicle in good working condition and avoiding costly repairs.
Here are some preventative maintenance tips to follow:
Follow the Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule
The manufacturer’s maintenance schedule outlines the recommended maintenance tasks for your vehicle.
It includes tasks such as oil changes, fluid flushes, and filter replacements.
Following this schedule ensures that your vehicle receives the necessary maintenance to keep it running smoothly.
Check Fluid Levels
Check the fluid levels in your vehicle, including oil, coolant, transmission fluid, and brake fluid.
Low fluid levels can cause severe vehicle problems, such as engine failure or brake failure.
Replace Filters Regularly
Air filters and fuel filters play a crucial role in keeping your engine running smoothly. Over time, these filters can become clogged, affecting engine performance.
Replace these filters according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
Check the Tires Regularly
Check the tire pressure and tread depth regularly. Low tire pressure can cause poor handling and decrease fuel efficiency.
Worn tire tread can reduce traction, especially in wet or snowy conditions, increasing the risk of accidents.
Address Issues Promptly
If you notice any issues with your vehicle, such as unusual noises or warning lights, address them promptly.
Ignoring these issues can lead to more severe vehicle problems and more costly repairs.
Keep Your Vehicle Clean
Keeping your vehicle clean, both inside and out, can prevent damage and increase its lifespan.
Regularly wash the exterior and clean the interior to prevent dirt and debris buildup that can cause wear and tear.
Store Your Vehicle Properly
If you’re storing your vehicle for an extended period, it’s essential to store it properly.
Use a vehicle cover to protect it from the elements and remove the battery to prevent it from draining.
FAQs
Can A Bad Starter Or Fuel Pump Damage Other Parts Of The Vehicle?
Yes, a bad starter or fuel pump can cause damage to other parts of the vehicle if not addressed promptly.
For example, a bad starter can cause damage to the flywheel, while a failing fuel pump can cause damage to the fuel injectors.
How Can I Prevent Starter Or Fuel Pump Issues?
Regular maintenance, including following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, checking fluid levels regularly, and addressing issues promptly, can help prevent starter or fuel pump issues.
Can I Replace A Starter Or Fuel Pump Myself?
While it is possible to replace a starter or fuel pump yourself, it is recommended to have it done by a professional mechanic to ensure that it is done correctly and safely.
How Much Does It Cost To Replace A Starter Or Fuel Pump?
The cost of replacing a starter or fuel pump can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle and the location of the repair.
On average, the cost can range from $300 to $800.
Final Words
A bad starter or fuel pump can be a frustrating issue to deal with, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can be easily diagnosed and fixed.
Understanding the differences between the two and knowing the symptoms to look for can save you time and money in the long run.
Remember to seek the advice of trusted experts and to always prioritize safety when working on your vehicle.
By taking these steps, you can get your car running smoothly again and avoid future breakdowns.
Don’t let a bad starter or fuel pump keep you off the road, tackle the issue head-on and get back to driving with confidence.
